History of Coconut
The coconut (Cocos nucifera) is a monotypic genus of palm tree cultivated primarily for its large edible nut. The coconut fruit is botanically classified as a monospermic drupe and is known for its versatility, providing food, water, fiber, and even serving as a flotation device. The coconut’s history is deeply intertwined with human migration and exploration. It is believed to have originated in the western Pacific, with evidence suggesting that it was brought under cultivation in two separate locations: the Pacific basin and the Indian Ocean basin
Case Studies of coconut
One of the most interesting case studies in coconut history is the discovery of its two distinct populations. A DNA analysis of over 1,300 coconuts from around the world revealed that these populations correspond to the Indian Ocean and Pacific basin, suggesting that the coconut was domesticated independently in these regions. This finding also preserved a record of prehistoric trade routes and the colonization of the Americas.
Different uses of Coconut
Coconuts have a wide range of uses across various industries. Here are some of the main categories and uses:
- Food and Beverages: Coconuts are used in cooking and baking, often in the form of coconut milk, coconut cream, or coconut oil. They are also used to make various dishes and desserts, such as coconut curries, coconut rice, coconut cakes, and coconut pies
- Cosmetics and Personal Care: Coconut oil is used in beauty products, including skincare, hair care, and makeup. It is known for its hydrating and nourishing properties, and is often used as a moisturizer, makeup remover, and hair conditioner
- Medicinal and Health Benefits: Coconut oil has been used in traditional medicine for various purposes, such as treating infections, wounds, and skin conditions. It is also believed to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, and is often used as a dietary supplement for its potential health benefits

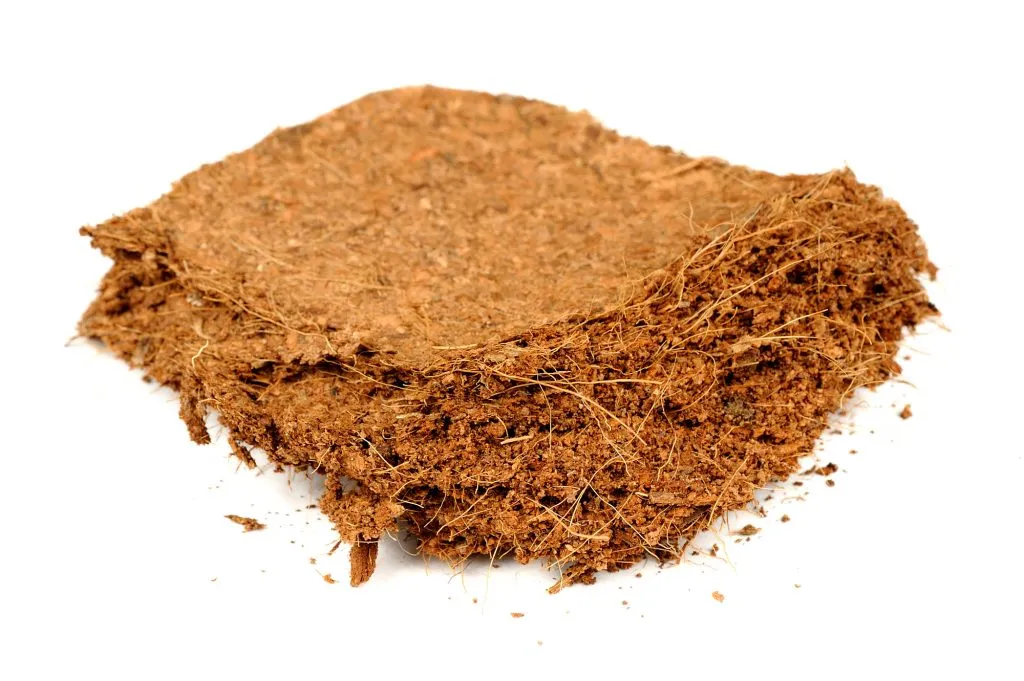
Industrial Applications: Coconut oil is used in the production of soaps, detergents, and other industrial products. The fibers from coconut husks are used to make rope, matting, and other textiles
Agriculture and Horticulture: Coconut palms are used as ornamental plants and are also used in landscaping. The leaves are sometimes used for thatching and roofing
Energy Production: The oil from coconuts can be used as a source of biofuel, and the husks can be used to produce biogas
Coconuts have a wide range of uses, from food and beverages to cosmetics, medicine, industry, agriculture, and energy production
Do you know – Both Coconut coir brick and Coconut coir grow bags uses same process of manufacturing
CVM Coir Substrates
Structure of Coconut
The coconut is not a nut but a drupe, and it has three main parts: the outer layer called the exocarp, the middle layer known as the mesocarp, and the inner hard layer called the endocarp.
The outer layer, the exocarp, is usually a shiny yellow-green to yellow-brown color.
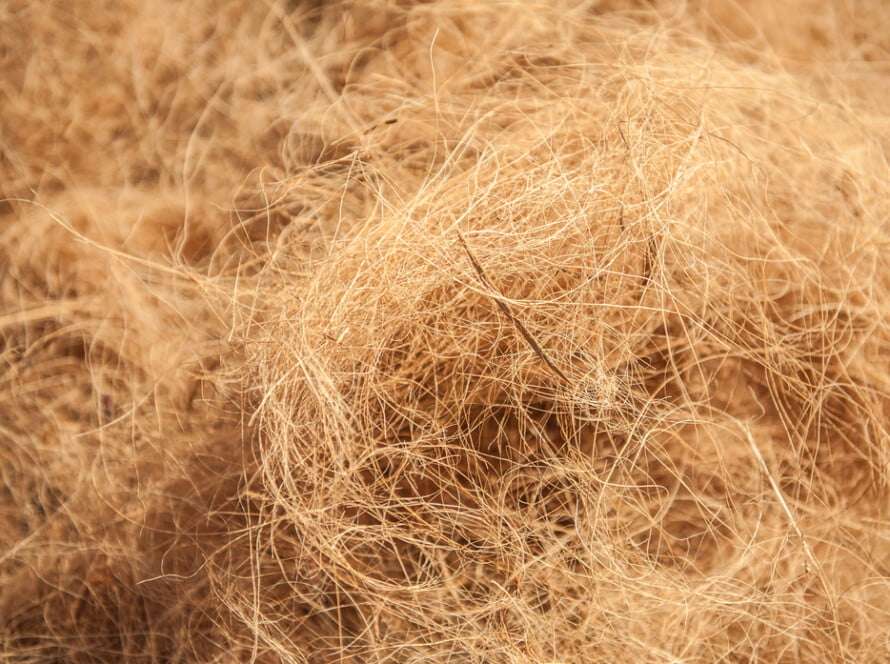
The middle layer, the mesocarp, is made up of coir fiber, which is widely used in traditional and commercial applications.
The innermost layer, the endocarp, is a tough, woody covering that surrounds the coconut flesh or endosperm.
The endocarp is about 4 millimeters thick and has three small holes for germination.
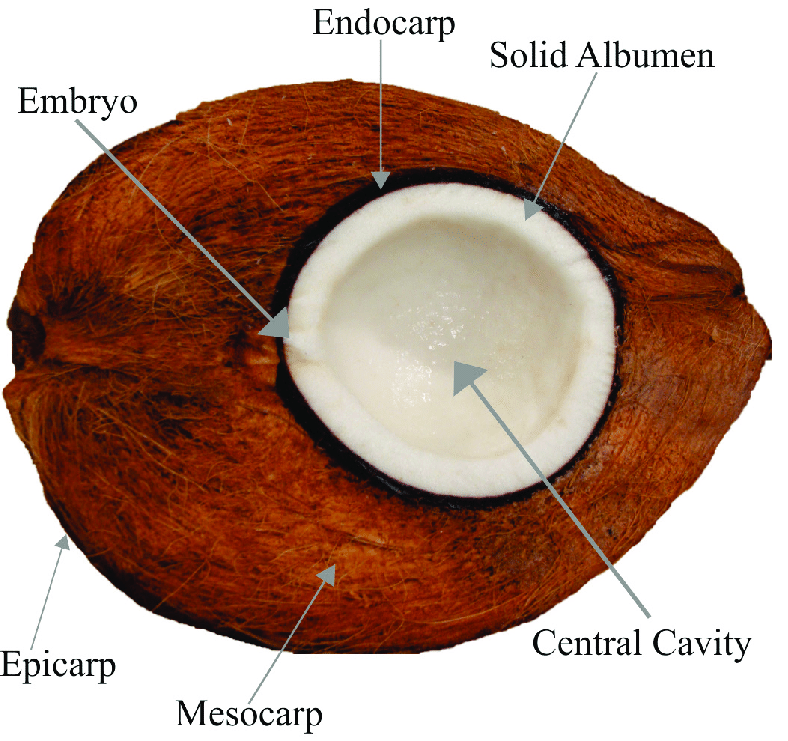

Inside the endocarp, there is a hollow space filled with coconut water, which is the liquid endosperm.
As the coconut matures, layers of solid endosperm, which is the coconut meat, form along the walls of the endocarp.
The embryo, a small cylindrical structure, is found within the solid endosperm.
When the coconut sprouts, the embryo emerges through a small opening in the endosperm.
The sprouting embryo develops into a haustorium inside the central cavity of the coconut.
Growing Mediums From Coconut
Coconut Coir: Coconut coir, also known as coco coir or Coco peat, is a versatile growing medium made from coconut husks. It holds water exceptionally well, is organic, and is ideal for growing grass, greens, and microgreens. It comes in brick form that expands when water is added, providing a loamy material for plant growth.
Coco Chips: Coco chips are another form of coconut coir, offering a different texture and size compared to coco peat. They can be used as a growing medium for plants, providing aeration and drainage for healthy root development.
Coco Fiber: Coconut fiber, also known as coco fiber, is a horticultural product made from coconut husks. It is used as a growing medium and can be mixed with soil or used alone. Coco fiber is beneficial for improving water retention and drainage in soil, making it a valuable addition to gardening projects.



